Dental Cyst Management
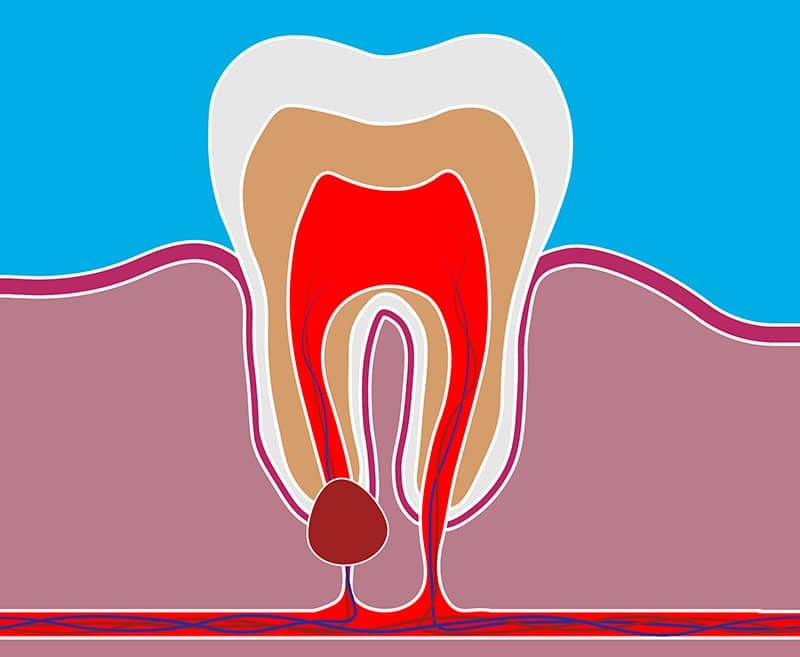
Dental cysts are frequently the result of a problem tooth or inflamed gum tissues. These tiny pockets of fluid can be sterile or contain infectious material. Dental cysts can be found in the gums, around impacted wisdom teeth, in the maxillary sinuses, or within the jawbone.
If you notice any unusual growths in your mouth or other issues with your dental health, please consult with your dentist. Getting early treatment could mean detecting a serious health problem or preventing future dental problems. The severity and cause of a dental cyst will determine the course of treatment.
Types of Dental Cysts:
Periapical Cyst (also known as an odontogenic or radicular cyst):
- It is the most common type of odontogenic cyst and is also known as a radicular cyst, apical periodontal cyst, root end cyst, or dental cyst.
- It is treated by endodontic therapy. If the endodontic treatment is not effective, the tooth is extracted, and the cyst is cleaned and filled with artificial bone material.
- Traditional methods were not effective enough as cysts continued to form. So, retrograde root canal filling is used according to the most modern treatment methods.
Follicular Cyst or Dentigerous Cyst:
- Most commonly, it is found in the area of the lower wisdom teeth or the permanent upper canines, which develop around the crown of an unerupted tooth.
- The pressure exerted by an erupting tooth on the follicle may cause the dentigerous cyst. This pressure can obstruct the blood flow and create an accumulation of fluid between the enamel membrane tissue and the coronal portion of the tooth.
- Dentigerous cysts usually grow and expand rapidly.
- The extraction of the associated tooth and the surgical excision of the cyst are often successful, and the patient is recalled to watch for recurrence.
Keratocystic Odontogenic Tumours (KCOTs):
- Keratocystic Odontogenic Tumors are most commonly found in the posterior area of the lower jaw or mandible and have similar characteristics to other types of cysts.
- A precise diagnosis can be made using only a biopsy, microscopic analysis, and a panoramic x-ray.
- Swelling is often the only symptom a patient will experience. There are several theories surrounding the origin of the keratocyst. Some experts believe the cyst develops in the place where the tooth should have been. Others argue that the tumours arise from the lamina of impacted teeth.
- Surgical excision is used with additional treatment. The patient is monitored throughout his lifetime to check for evidence of recurrence.
How is Dental Cysts Treated?
There are two ways to treat a dental cyst:
- Surgery – To remove all types of cysts or tumours.
- Endodontic Therapy – This is done in conjunction with surgical removal if the cyst is associated with an infected root canal.
Surgical Management of Dental Cysts:
- Detection: Dental cysts are normally picked up during a routine examination, which includes dental x-rays. Your dentist may order a 3D CBCT scan for more information about the cyst and its relationship with surrounding teeth and other structures (nerves, sinuses) within the bone.
- Pre-surgical Preparation: Scaling and polishing are performed a few days before surgery. To ensure that healing proceeds smoothly, an oral probiotic is given to increase the number of beneficial bacteria in the saliva. If root canal treatment is required, it will be completed before surgery.
- Removing The Cyst: Under local anaesthesia, an oral surgeon removes the cyst through a window in the bone. You can also be sedated throughout the procedure to ensure a stress-free experience. If there is a tooth embedded within the cyst, it may be extracted as well. The bone grafting material may also be used to fill the void left by cyst removal. Following that, stitches will be placed in the gums. After a few days, these will be removed.
The excised tissue can be sent to a pathology lab for identification using a microscope. This is critical for distinguishing other types of tumours that may resemble cysts.